
BBE 1st Grade Science Lab! Gardening & Plant parts
Definition of Seed: A true seed is defined as a fertilized mature ovule that possesses embryonic plant, stored material, and a protective coat or coats. Seed is the reproductive structure characteristic of all phanerogams. The structure of seeds may be studied in such common types of pea, gram, bean almond or sunflower.
Parts of a Seed Labelled diagram
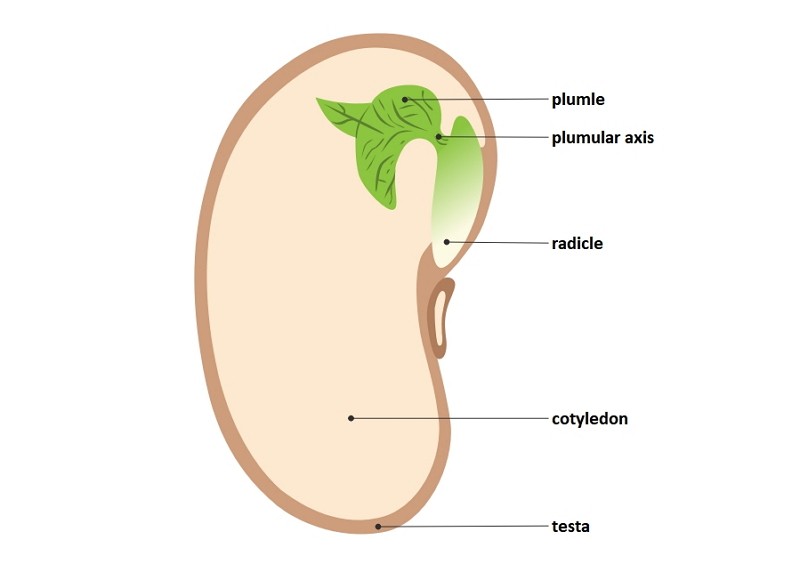
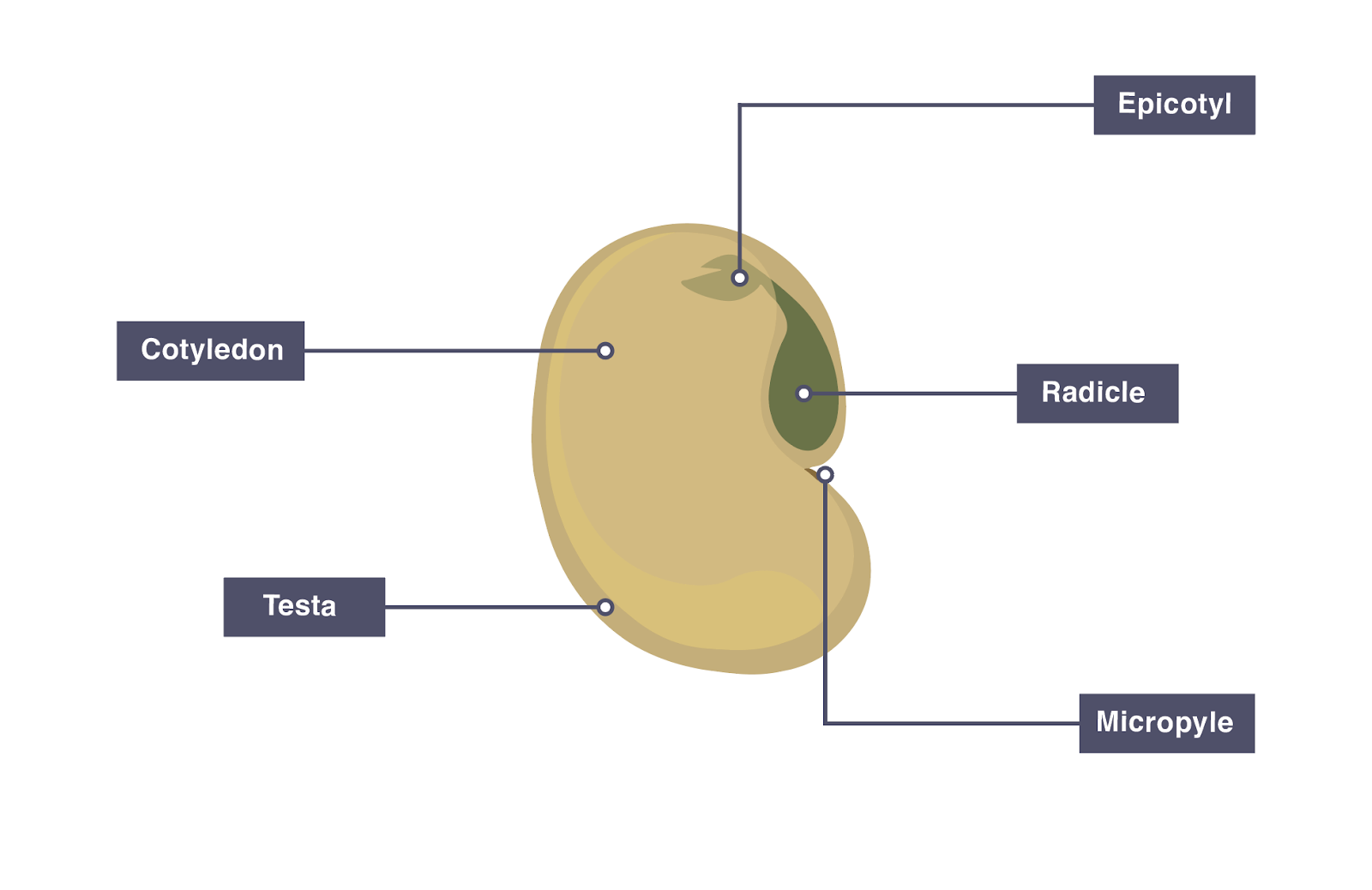
A typical seed consists of the following parts: Source: Google. Tesla: It is the outer coat of the seed that protects the embryonic plant. Micropyle: It is a tiny pore in the testa that lies on the opposite of the tip of the radicle. It permits water to enter the embryo before active germination. Hilum: Is a scar left by the stalk which.

Parts Of A Seed Printable Printable Word Searches
Most fruits have seeds, which make them capable of developing into new plants. Find out more with Bitesize. For students between the ages of 11 and 14.

MySci Unit 06 Seeds, Sprouts and Sunshine (PREVIEW Interactive
A typical seed will possess the following features: Testa - an outer seed coat that protects the embryonic plant. Micropyle - a small pore in the outer covering of the seed, that allows for the passage of water. Cotyledon - contains the food stores for the seed and forms the embryonic leaves. Plumule - the embryonic shoot (also called.
A Guide to Understand Seed with Diagram EdrawMax Online
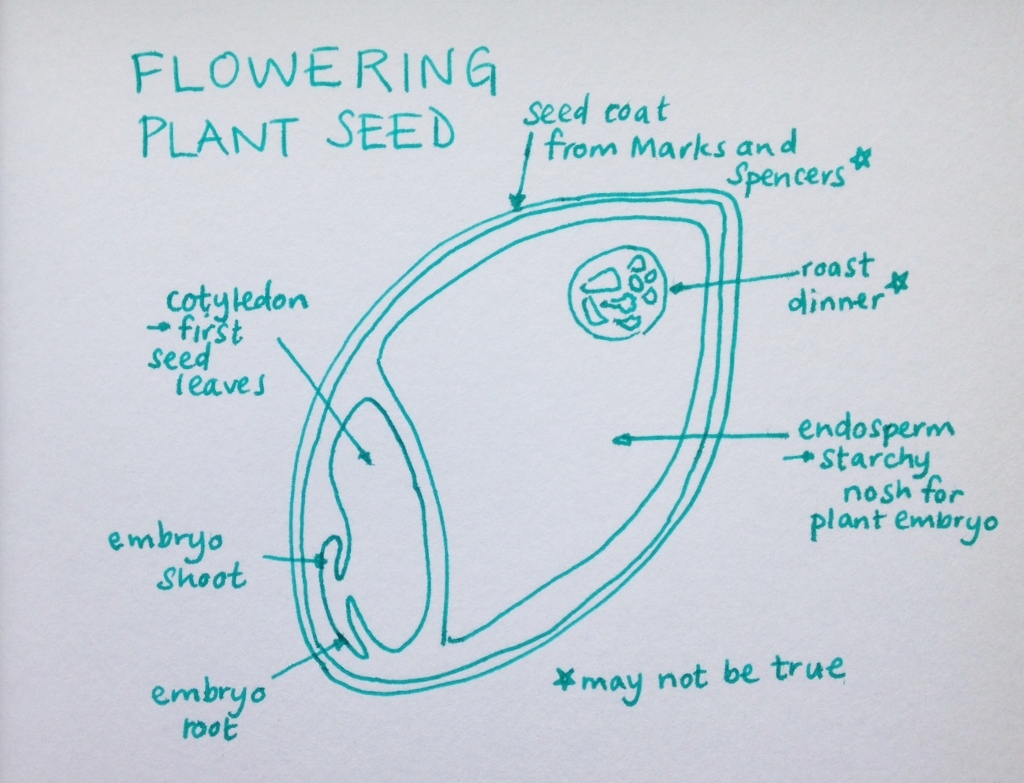
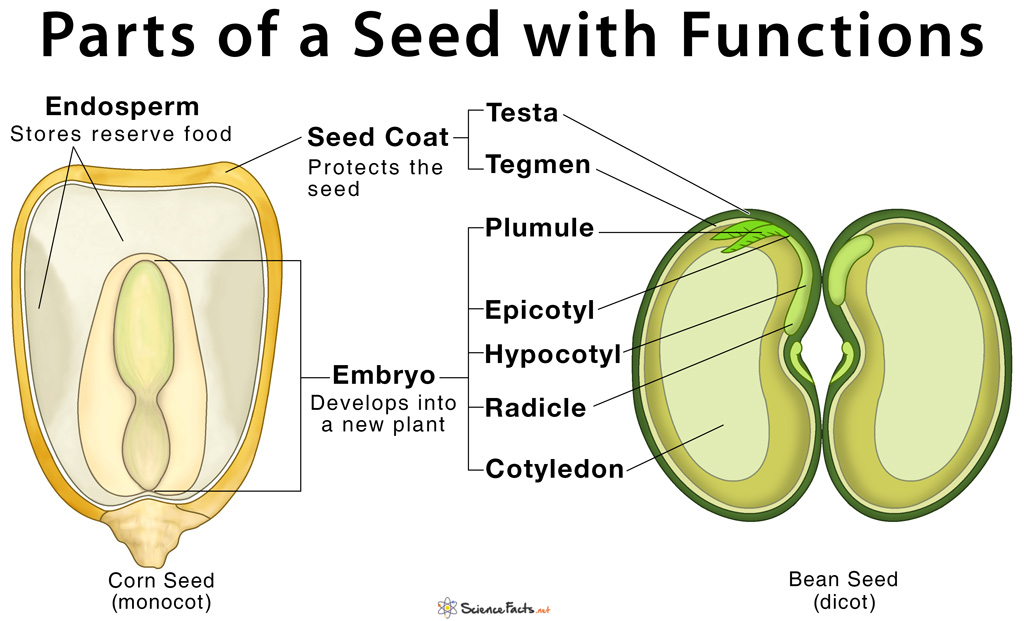
Parts of a Seed Diagram A typical seed consists of three main parts: 1) seed coat, 2) endosperm, and 3) embryo. 1) Seed Coat They are the protective outer covering of a seed that is usually hard, thick, and brownish in color. The seed coat is formed from the outer covering of the ovule called the integument.

Germination of Seed Diagram CBSE Class Notes Online Classnotes123
The micropyle is a small round structure next to the hilum where the pollen tube entered. Figure 4.6.3.1 4.6.3. 1: The external structures of a bean seed, an example of a eudicot (7X). The seed coat surrounds the seed. There is a round micropyle, where the pollen tube originally entered the ovule.
Seed Germination Definition, Steps, & Factors Affecting Them
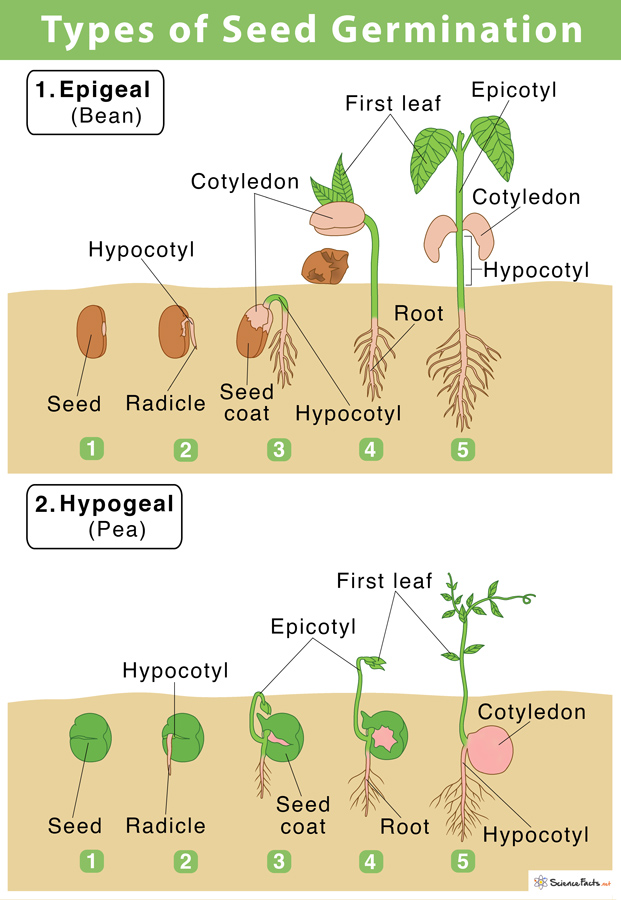
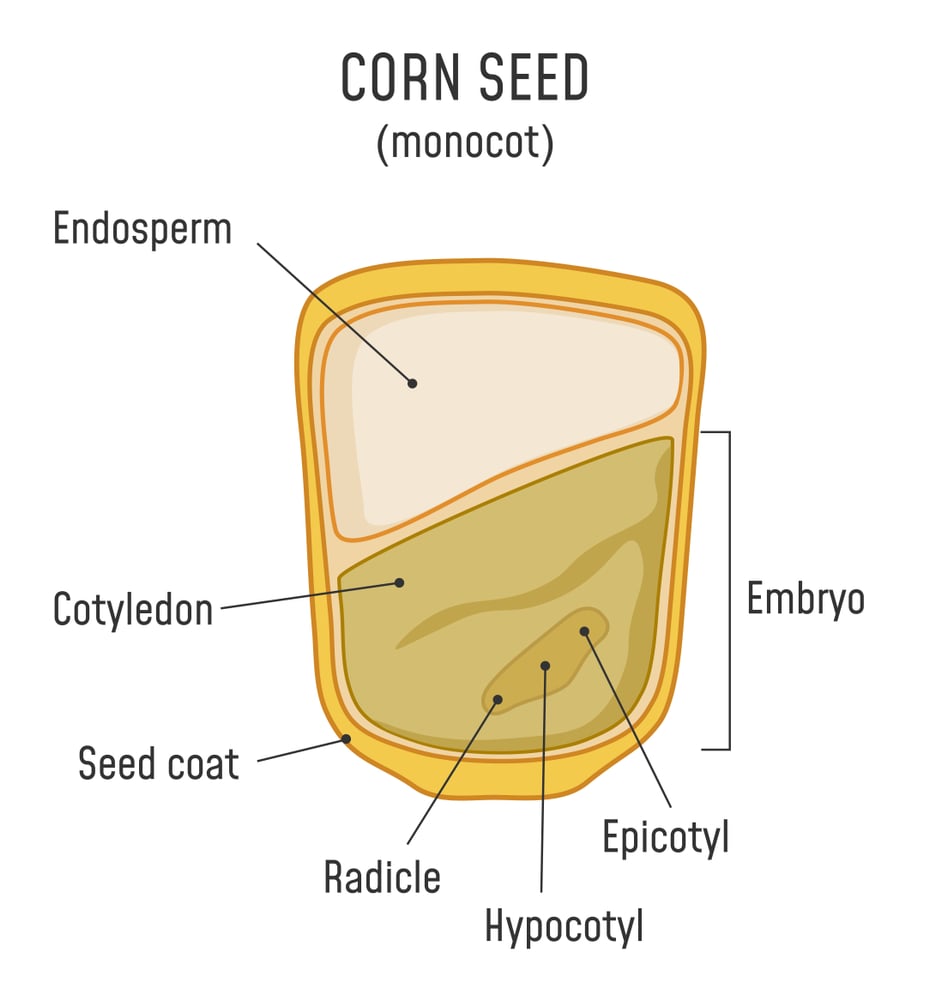
Germination involves the following steps: Seeds swell, plumules develop into shoots From the radicle of the seeds, the roots arise Formation of cotyledons (one in monocots and two in dicots) Material Required Seeds of red kidney bean/gram Forceps Magnifying glass Cloth Petri dish
The wonder of seeds, by the Higgledy newbie (Emma) Higgledy Garden
Seed Growth. In angiosperms, the process of seed development begins with double fertilization and involves the fusion of the egg and sperm nuclei into a zygote. The second part of this process is the fusion of the polar nuclei with a second sperm cell nucleus, thus forming a primary endosperm. Right after fertilization, the zygote is mostly.

Anatomy Of A Bean Seed Stock Vector Art & More Images of Agriculture
It consists of three parts: a plumule that forms the shoot, a hypocotyl that forms the stem, and a radicle that forms the root. Structures of dicot and monocot seeds - LibreTexts (CC BY-NC-SA) The seed coat consists of one (in monocots) or more (in dicots) protective layers that encase the seed. In dicots, the seed coat is divided into an.
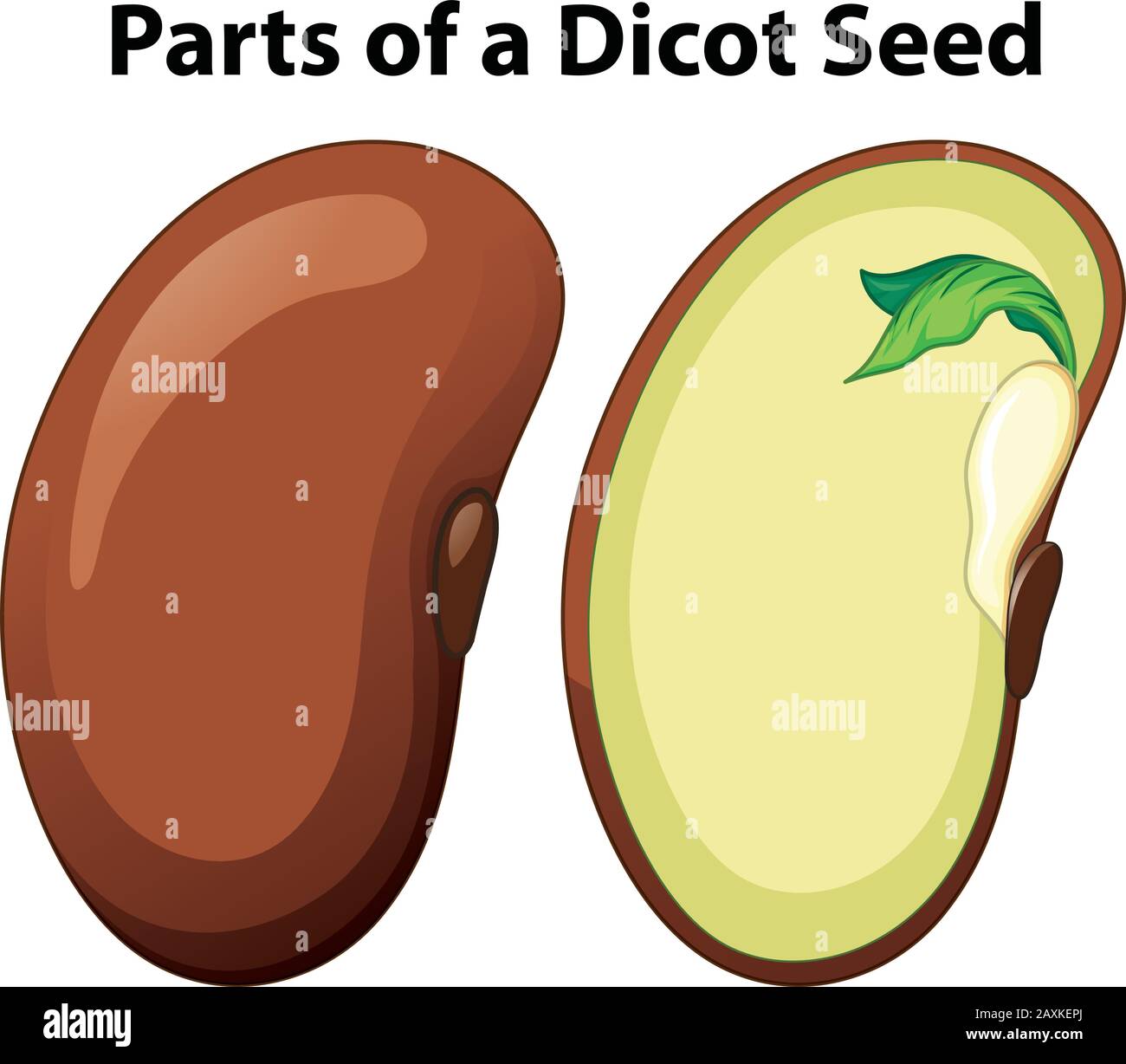
Diagram showing parts of dicot seed on white background illustration
Endospermic seed structure (Eudicots): Brassicaceae - Lepidium sativum as model system in seed biology : In mature seeds of Lepidium sativum (garden cress) the embryo is surrounded by 1-2 cell layers of endosperm. FA2-type seed. We found that Lepidium seeds exhibit, as tobacco, a two-step germination process with distinct testa rupture and endosperm rupture.
Parts of a Seed, Their Structure, and Functions with Diagram
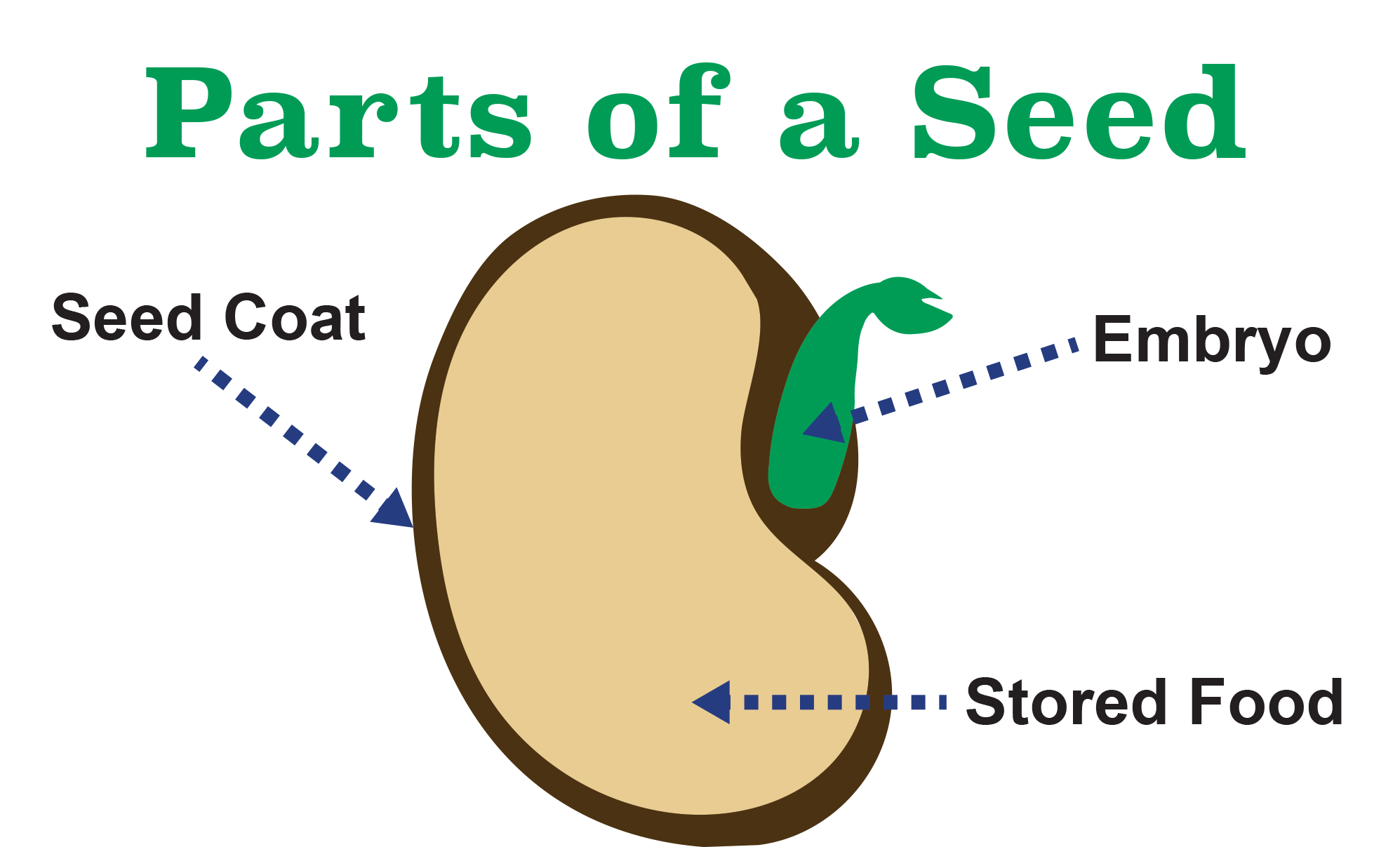
Seed Anatomy Seeing Seeds Close-up - These pictures are of a pea seed Here you can see, I've removed the seed coat and split the seed in half. One half has the embryo and some of the stored food, and the other half holds the rest of the stored food. This picture is of the half of the seed that has the embryo.

Parts Of A Seed cloudshareinfo
Essentially, a seed consists of a miniature undeveloped plant (the embryo), which, alone or in the company of stored food for its early development after germination, is surrounded by a protective coat (the testa).
Seed Coat Functions Protection and Beyond revolutionseeds
6 days ago The perfect follow-up for a dissection! Learn about the parts of a seed and draw your own diagram.
[DIAGRAM] Apple Seed Diagram
Seeds and diversity. To review, the two fundamental ways of propagating plants and how they differ in their outcomes are s exual reproduction through seeds or spores, and a sexual or vegetative reproduction through manipulation of various plant parts, including cuttings from leaves, roots, and stems, or grafting.. Asexual reproduction, also called vegetative propagation, normally results in.
IGCSE Biology 2017 3.6 Understand How Germinating Seeds Utilise Food
A seed, in botanical terms, is an embryonic plant enclosed inside its seed coat . Typically, the seed also has stored energy (proteins and carbohydrates) that are used by the seed during germination to establish itself when environmental conditions are favorable for growth. The stored energy is what makes seeds valuable for humans, too.

Seed Germination Process, Stages of Germination, Factors
Diagram of a generalized dicot seed (1) versus a generalized monocot seed (2). A. Scutellum B. Cotyledon C. Hilum D. Plumule E. Radicle F. Endosperm Comparison of monocotyledons and dicotyledons Embryo. In endospermic seeds, there are two distinct regions inside the seed coat, an upper and larger endosperm and a lower smaller embryo.