Cholangitis as related to Cholecystitis Pictures
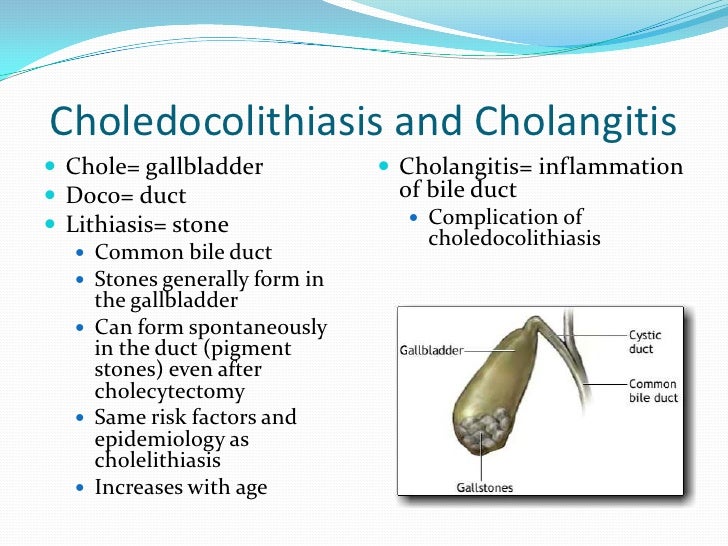
Individuals with acute cholecystitis present with right upper quadrant pain, fever, and leukocytosis. Management includes supportive care and cholecystectomy. The prevalence of choledocholithiasis is 10% to 20%, and serious complications include cholangitis and gallstone pancreatitis.

The Right Code for Acute Cholecystitis and Cholelithiasis
3. In patients with large choledocholithiasis, is endoscopic papillary dilation after sphincterotomy favored over sphincterotomy alone? 4. What is the role of ERCP-guided intraductal therapy (EHL and laser lithotripsy) in patients with large and difficult choledocholithiasis? Five additional clinical questions were addressed by the

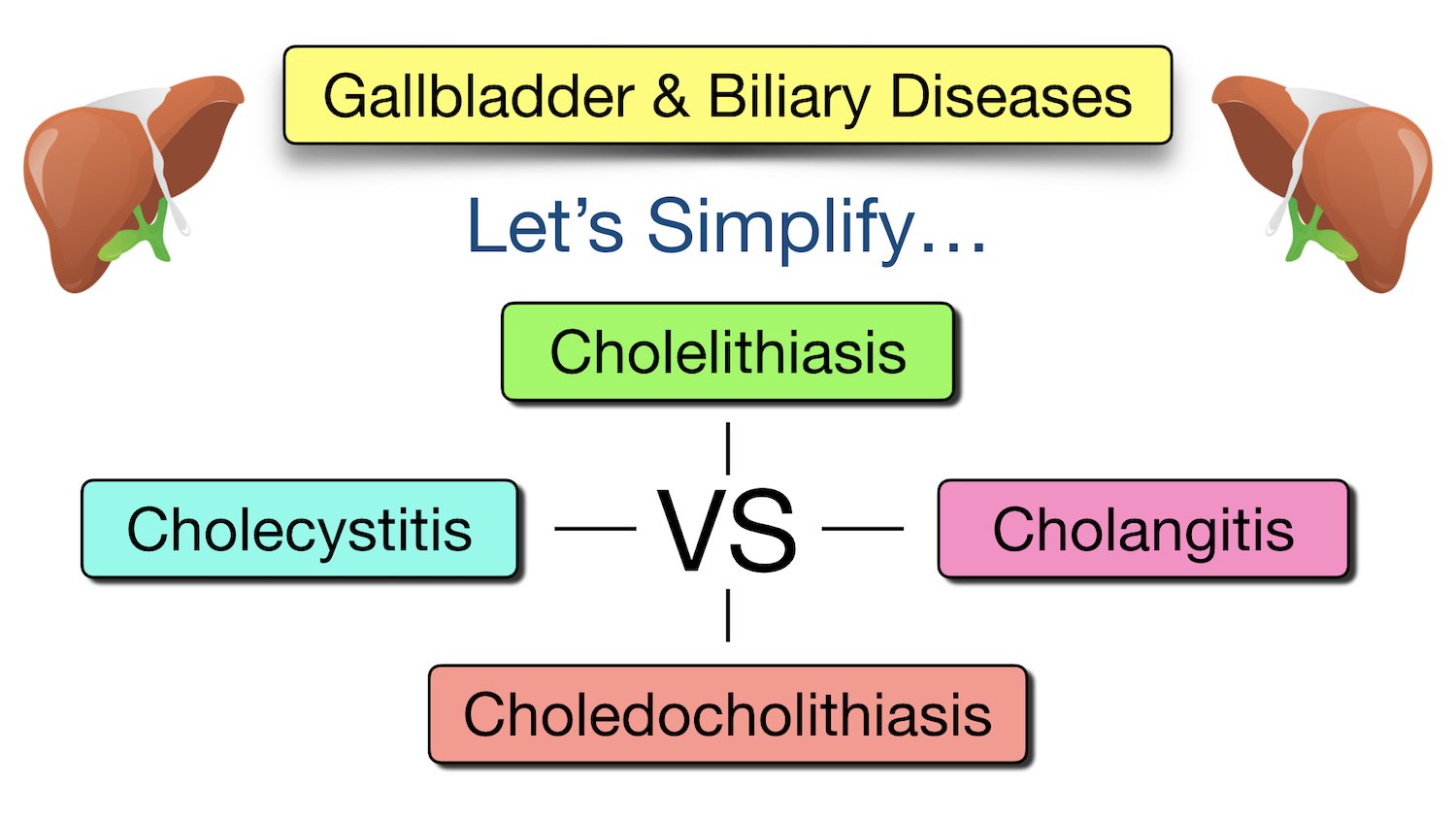
Cholelithiasis vs Cholecystitis vs Choledocholithiasis vs Cholangitis
Cholelithiasis is the presence of one or more calculi (gallstones) in the gallbladder. Gallstones tend to be asymptomatic. The most common symptom is biliary colic; gallstones do not cause dyspepsia or fatty food intolerance. More serious complications include cholecystitis; biliary tract obstruction (by stones in the bile ducts.
Choledocholithiasis obstructive jaundice
Acute cholecystitis is a syndrome of right upper quadrant pain, fever, and leukocytosis associated with gallbladder inflammation. It typically occurs in patients with gallstones (ie, acute calculous cholecystitis [ACC]), while acalculous cholecystitis accounts for a minority (5 to 10 percent) of cases. Complications of acute cholecystitis.
Made Easy Cholelithiasis vs Cholecystitis vs Choledocholithiasis vs
Major symptoms: (1) biliary colic—a severe steady ache in the RUQ or epigastrium that begins suddenly; often occurs 30-90 min after meals, lasts for several hours, and occasionally radiates to the right scapula or back; (2) nausea, vomiting. Physical examination may be normal or show epigastric or RUQ tenderness. LABORATORY

Pin on GI Review
The role of CT and MRI in the evaluation of cholecystitis, choledocholithiasis, and the hyperplastic cholecystoses is discussed. Cholelithiasis Pathogenesis and Epidemiology . The prevalence of gallstones varies with age and gender. Gallstones are present in an estimated 10% to 15% of men and 20% to 40% of women older than 60 years.

Medicine For Gallstones Online Sellers, Save 57 jlcatj.gob.mx
Abdominal muscle stiffness on the right side. Weakness and fatigue, especially in older people. Chronic cholecystitis symptoms tend to be less severe, and they come and go. You might have an episode of biliary colic — abdominal pain with nausea — after a rich or heavy meal. Fatty foods require more bile to digest.

Cholecystitis vs Choledocholithiasis vs Ascending Cholangitis [
Treatment and prognosis. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with sphincterotomy is the treatment of choice for choledocholithiasis, however, is associated with a complication rate of 5.8-24% (10 years follow-up) 1. Complications of ERCP and sphincterotomy include: acute pancreatitis. acute cholangitis.

Medical Biotechnology on Instagram “Choledocholithiasis
Acute calculous cholecystitis (ACC) is the most frequent complication of gallstones requiring cholecystectomy. These patients may have coexisting choledocholithiasis. We aimed to evaluate the role of current guidelines for choledocholithiasis in patients with ACC. Methods
Colecistitis Colangitis Coledocolitiasis Quiz Quizizz Sexiz Pix
Cholecystitis (ko-luh-sis-TIE-tis) is inflammation of the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of the belly (abdomen), beneath the liver. The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid (bile) that's released into the small intestine.
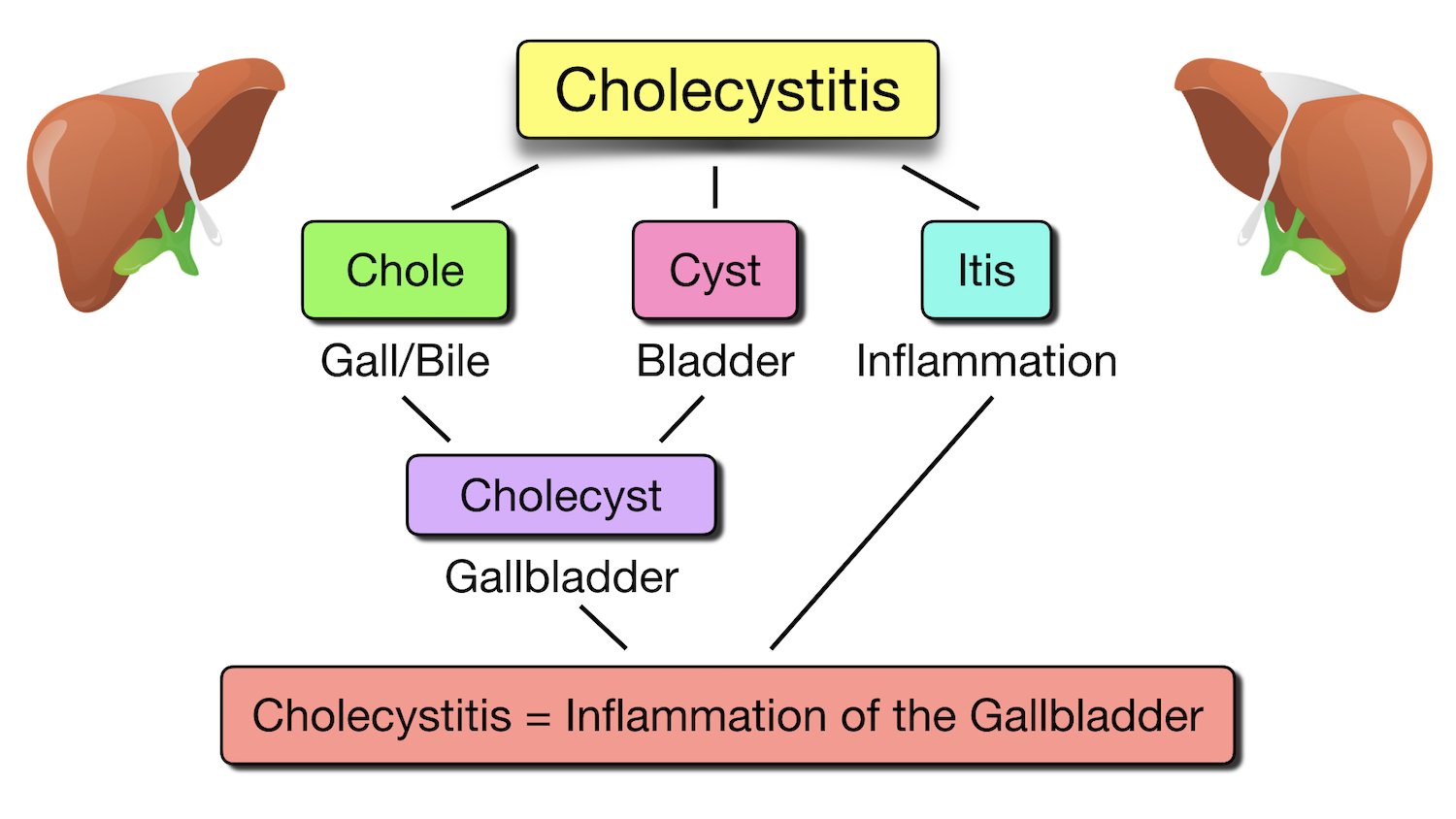
Made Easy Cholelithiasis vs Cholecystitis vs Choledocholithiasis vs
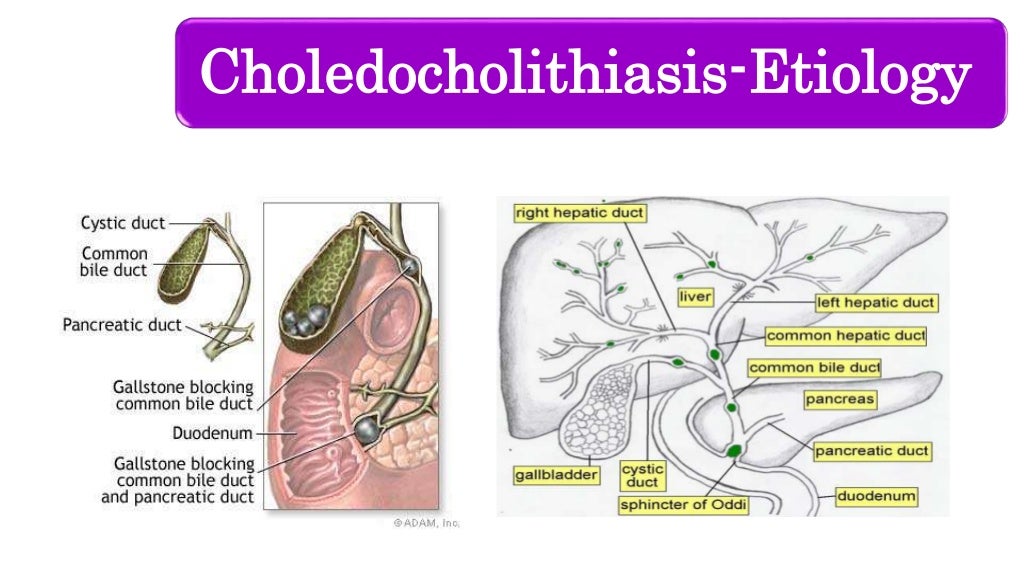
INTRODUCTION Choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of gallstones within the common bile duct. This topic will review the clinical manifestations and diagnosis of choledocholithiasis. The treatment of choledocholithiasis, as well as the epidemiology and the general management of patients with gallstones, are discussed separately:
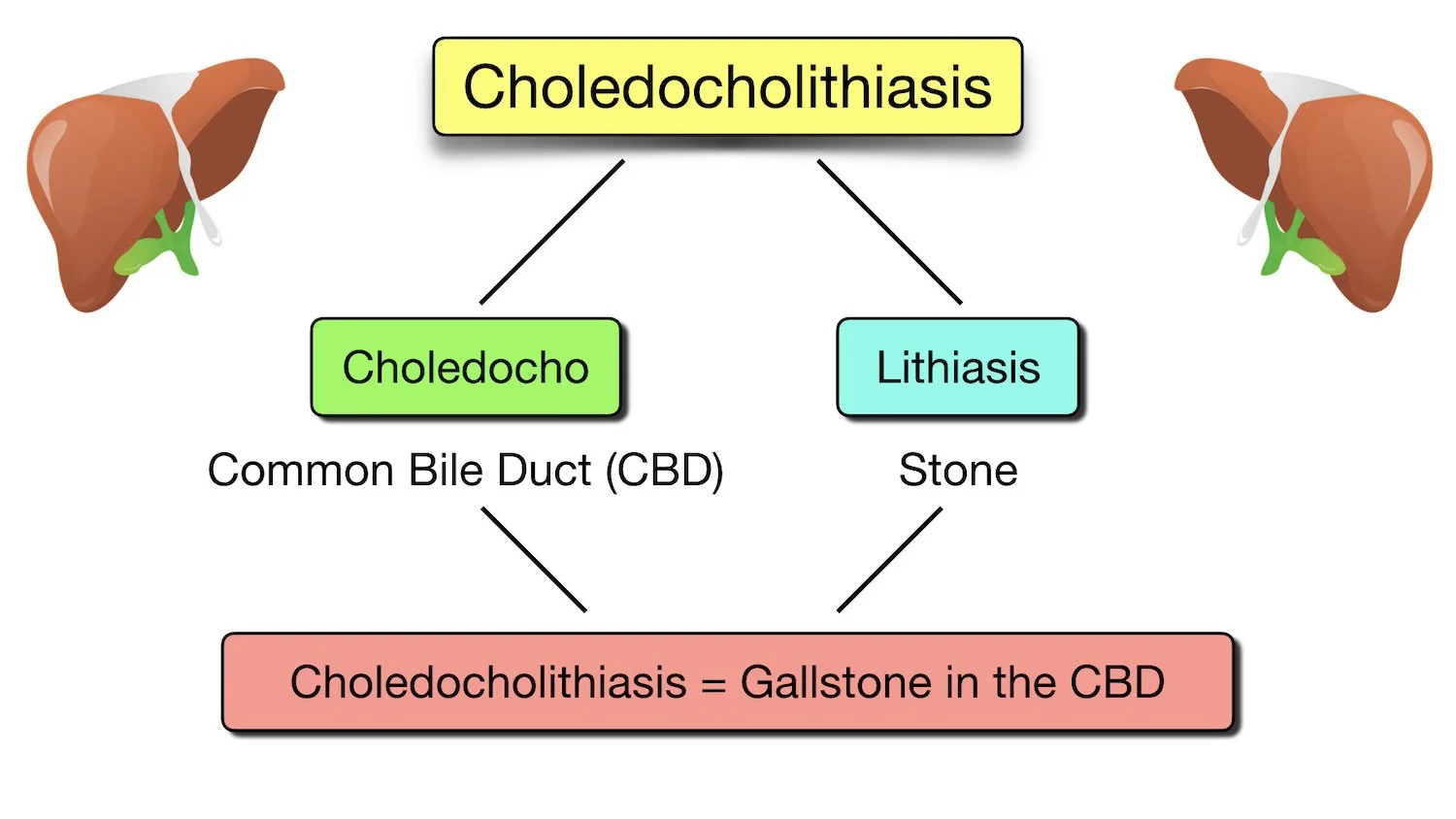
Made Easy Cholelithiasis vs Cholecystitis vs Choledocholithiasis vs
Cholecystolithiasis — "Cholecystolithiasis" refers to the presence of stones in the gallbladder. The presence of stones in the gallbladder is not considered to be a disease unless they cause symptoms. Gallstone disease — The term "gallstone disease" refers to gallstones that cause symptoms. (See 'Clinical manifestations' below.)

Cholecystitis vs Cholelithiasis vs Cholangitis vs Choledocholithiasis
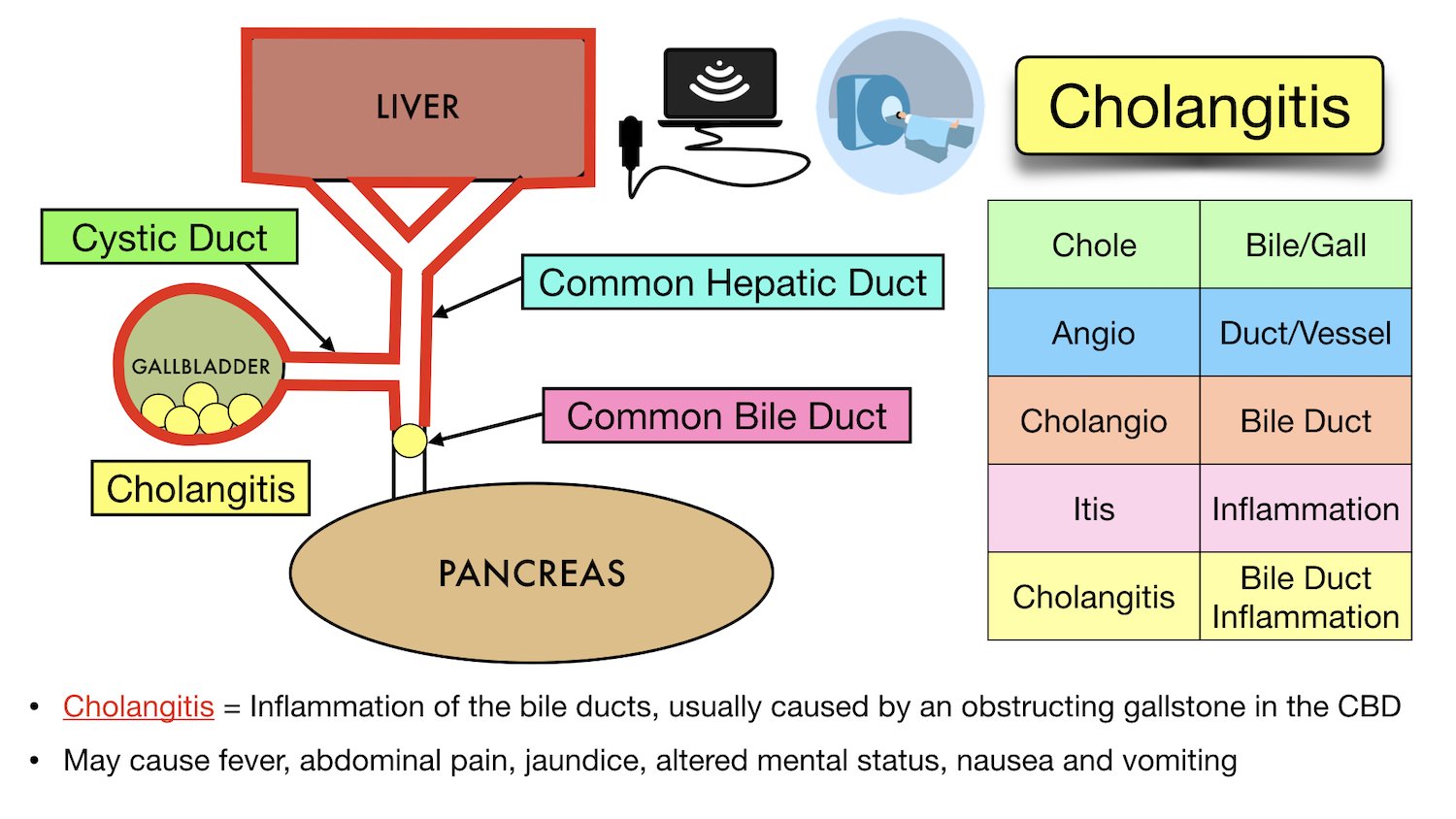
Key Points Choledocholithiasis is the presence of stones in bile ducts; the stones can form in the gallbladder or in the ducts themselves. These stones cause biliary colic, biliary obstruction, gallstone pancreatitis, or cholangitis (bile duct infection and inflammation).
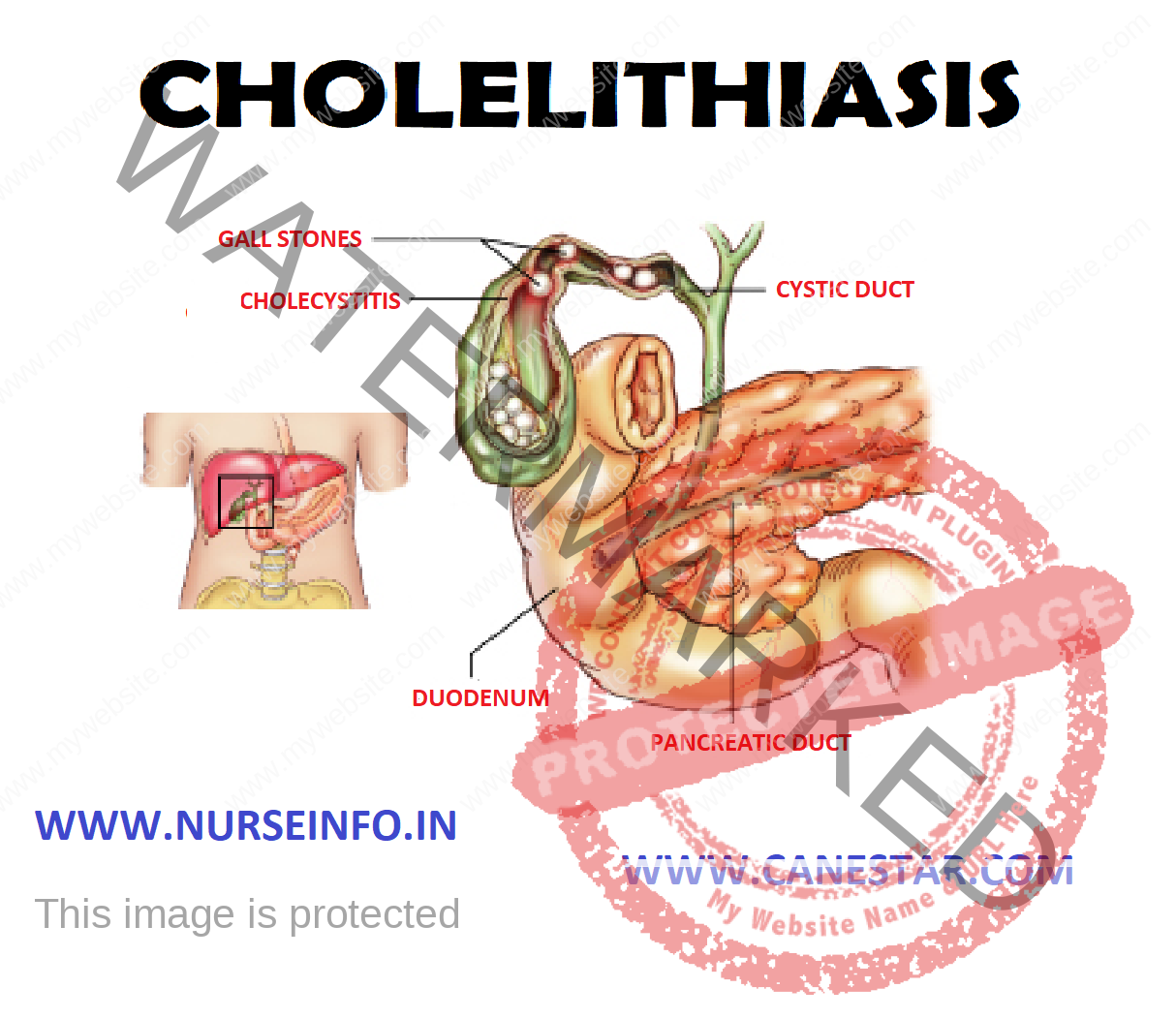
CHOLELITHIASIS AND CHOLECYSTITIS Nurse Info
Introduction When learning about the gallbladder and biliary system, the terms cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, choledocholithiasis, and cholangitis sound similar yet are very different disease states. Let's walk through each one step by step using illustrations and strategies that will help clarify the pathology. Biliary Anatomy

Gallbladder Inflammation or Blocked Bile Ducts Understanding Acute
Choledocholithiasis is the presence of stones within the common bile duct (CBD). It is estimated that common bile duct stones are present in anywhere from 1-15% of patients with cholelithiasis.

Acute cholecystitis as related to Cholangitis Pictures
Choledocholithiasis, also known as common bile duct stones, refers to an obstruction of the biliary tract caused by gallstones in the common bile duct. The common bile duct is the tube that carries bile from the liver to the small intestine, and it is formed by the union of the common hepatic duct and the cystic duct.